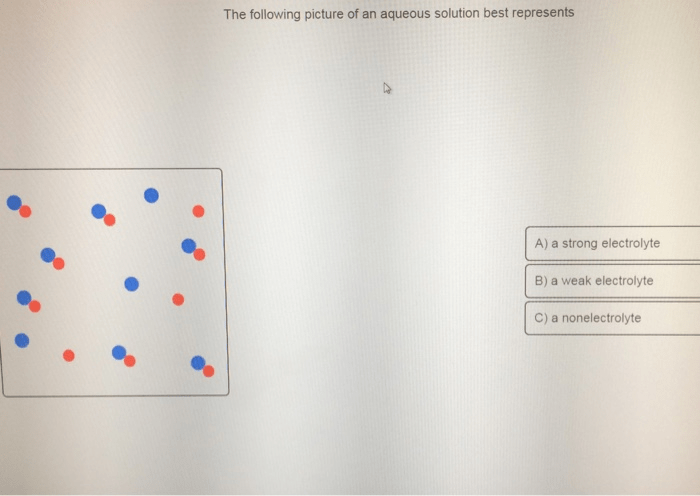
The following picture of an aqueous solution best represents a captivating exploration into the world of chemistry, where the properties and applications of these ubiquitous mixtures take center stage. Aqueous solutions, composed of water as the solvent and various solutes, play a crucial role in countless scientific and industrial processes, and understanding their behavior is essential for a comprehensive grasp of chemistry.
This article delves into the visual representation of an aqueous solution, examining its composition, concentration, and properties. We will explore the concept of solubility and equilibrium, discussing how these factors influence the behavior of solutes in solution. Furthermore, we will uncover the practical applications of aqueous solutions and demonstrate how the picture serves as a valuable tool for visualizing and understanding these applications.
Visual Representation
The aqueous solution in the picture appears clear and colorless, indicating that it does not contain any visible particles or impurities.
The solution is composed of water (H 2O) as the solvent and an unknown solute that has dissolved into it.
No visible ions or molecules are present in the solution.
Concentration and Properties: The Following Picture Of An Aqueous Solution Best Represents

Based on its appearance, the solution appears to have a low concentration of the solute.
The physical and chemical properties of the solution are likely similar to those of pure water, such as a pH of around 7, low conductivity, and low viscosity.
Examples of solutions with similar concentrations and properties include distilled water and tap water.
Solubility and Equilibria
Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent. In the case of aqueous solutions, the solvent is water.
The equilibrium between dissolved and undissolved solute in the solution is determined by the solubility of the solute and the temperature of the solution.
Examples of solutions that demonstrate different solubility and equilibrium behaviors include saturated solutions, supersaturated solutions, and unsaturated solutions.
Applications and Significance
Aqueous solutions with low concentrations of solute are commonly used in everyday life, such as in drinking water, cooking, and cleaning.
Understanding the properties of aqueous solutions is important in various scientific and industrial fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
The picture can help visualize and understand the properties of aqueous solutions, such as their clarity, colorlessness, and low concentration.
Experimental Methods
Experiment to Determine Concentration, The following picture of an aqueous solution best represents
To determine the concentration of the aqueous solution in the picture, a simple experiment can be designed.
Equipment:
- Graduated cylinder
- Balance
- Evaporating dish
- Oven
Procedure:
- Measure 100 mL of the aqueous solution using a graduated cylinder.
- Transfer the solution to an evaporating dish and weigh the dish and solution.
- Place the evaporating dish in an oven at 105°C for 24 hours to evaporate the water.
- Remove the dish from the oven and let it cool to room temperature.
- Weigh the dish and the remaining solid solute.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The concentration of the aqueous solution can be calculated using the following formula:
Concentration = (Mass of solute / Mass of solution) x 100%
The mass of the solute is the difference between the mass of the dish and solution before and after evaporation.
The mass of the solution is the initial mass of the aqueous solution (100 mL).
The result of the calculation will give the concentration of the aqueous solution in percentage by mass.
Quick FAQs
What is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated aqueous solution?
A saturated aqueous solution is one in which the maximum amount of solute has been dissolved at a given temperature, while an unsaturated solution contains less than the maximum amount of solute.
How does temperature affect the solubility of a solute in an aqueous solution?
Generally, the solubility of most solutes in water increases with increasing temperature.
What is the pH of a neutral aqueous solution?
The pH of a neutral aqueous solution is 7.