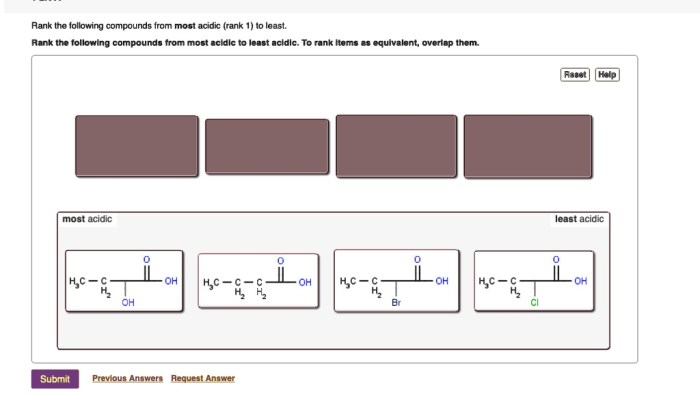
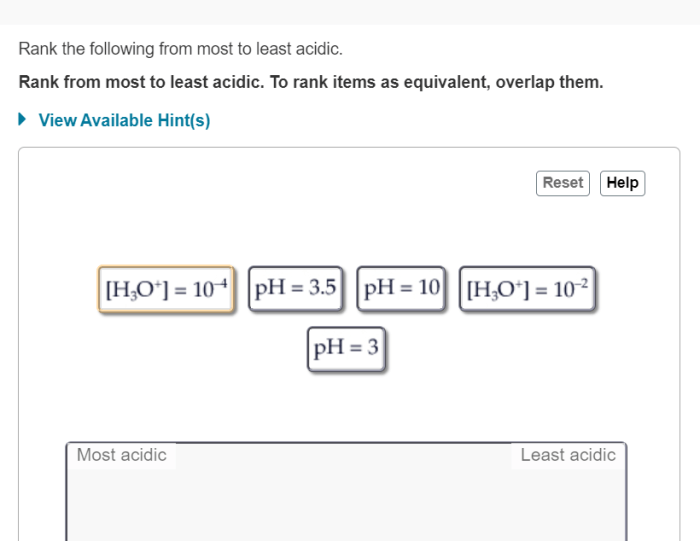
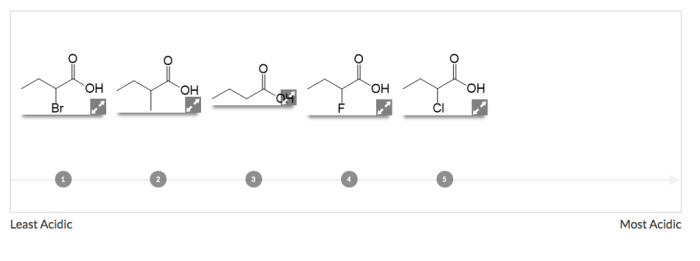
Rank the following acids from least acidic to most acidic – The ranking of acids is a crucial concept in chemistry, providing insights into the behavior and properties of various acidic substances. This ranking is based on the acidity scale, which measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution and determines its acidity level.
Understanding the factors influencing acidity and the ranking of acids is essential in numerous fields, including chemistry, biology, medicine, and industrial processes.
Acidity is a measure of the ability of a substance to donate protons (H+ ions). The lower the pH value, the higher the acidity. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic.
Acids have a pH less than 7, while bases have a pH greater than 7.
Acidity Scale
The acidity of a solution is measured on a scale called the pH scale. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic (or alkaline). A pH of 7 is considered neutral.
The pH of a solution is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the solution. The higher the concentration of H+ ions, the lower the pH and the more acidic the solution.
Factors Affecting Acidity
The acidity of a solution is influenced by several factors, including:
- Concentration of hydrogen ions (H+):The higher the concentration of H+ ions, the lower the pH and the more acidic the solution.
- Dissociation constant (Ka):The dissociation constant is a measure of the strength of an acid. A stronger acid has a higher Ka and dissociates more completely in water, resulting in a lower pH.
- Temperature:The acidity of a solution can change with temperature. In general, the acidity of a solution decreases as the temperature increases.
Ranking Acids, Rank the following acids from least acidic to most acidic
The following table ranks the given acids from least acidic to most acidic:
| Acid | pH |
|---|---|
| Carbonic acid (H2CO3) | 6.3 |
| Acetic acid (CH3COOH) | 4.7 |
| Nitric acid (HNO3) | 1.0 |
| Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) | -2.0 |
| Hydrochloric acid (HCl) | -1.0 |
Applications of Acid Ranking
The ranking of acids is useful in various fields, including:
- Chemistry:Acid ranking is used to predict the reactivity of acids and to design chemical reactions.
- Biology:Acid ranking is used to understand the pH of biological fluids and to study the effects of acids on living organisms.
- Medicine:Acid ranking is used to develop drugs and to treat diseases that are caused by acid-base imbalances.
- Industrial processes:Acid ranking is used to optimize industrial processes that involve acids, such as metalworking and food processing.
Exceptions and Limitations
There are some exceptions and limitations to the ranking of acids. For example:
- Non-aqueous solutions:The pH scale is only valid for aqueous solutions. In non-aqueous solutions, the acidity of a solution may not be accurately represented by the pH scale.
- Mixtures of acids:When two or more acids are mixed, the acidity of the solution may not be simply the average of the individual acids. The acidity of the mixture will depend on the relative concentrations and strengths of the acids.
- Weak acids with high concentrations:In some cases, a weak acid with a high concentration may be more acidic than a strong acid with a low concentration.
FAQ Overview: Rank The Following Acids From Least Acidic To Most Acidic
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic.
What is the relationship between pH and acidity?
The lower the pH value, the higher the acidity. This is because a lower pH indicates a higher concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the solution.
What are the factors that affect the acidity of a solution?
The acidity of a solution is affected by several factors, including the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), the dissociation constant (Ka), and the temperature.