Dna rna and protein synthesis worksheet answer key – DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis worksheet answer key sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of molecular biology, exploring the structure and function of DNA, RNA, and proteins, as well as the fundamental processes of transcription and translation.
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the heart of cellular machinery, where the blueprints of life are meticulously crafted.
DNA Structure and Function: Dna Rna And Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key

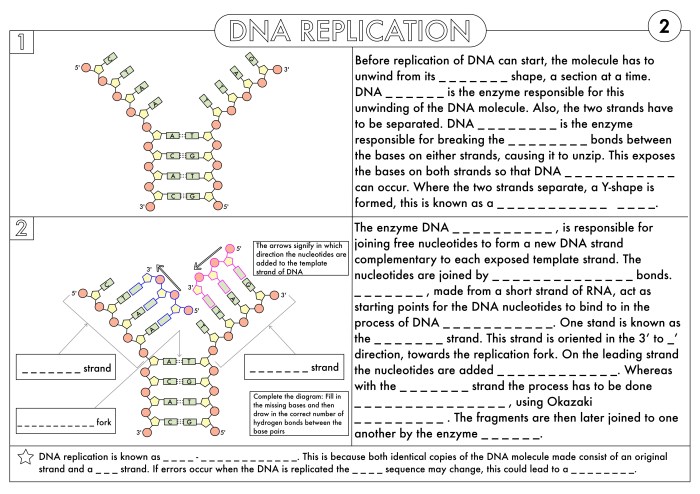
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA is a polymer made from a chain of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases pair up with each other to form base pairs, which are the building blocks of DNA. Adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
DNA is organized into genes, which are regions of DNA that code for a specific protein. Genes are located on chromosomes, which are long, thin structures found in the nucleus of cells. Each chromosome contains many genes, and each gene contains the instructions for making a specific protein.
RNA Structure and Function
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a molecule that is similar to DNA but has a different structure and function. RNA is a polymer made from a chain of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
The four nitrogenous bases found in RNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). Uracil replaces thymine in RNA. RNA is also typically single-stranded, while DNA is double-stranded.
There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are made. tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes in the correct order, as specified by the mRNA.
rRNA is a component of the ribosomes.
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Brings amino acids to the ribosomes in the correct order, as specified by the mRNA.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): A component of the ribosomes.
Protein Synthesis, Dna rna and protein synthesis worksheet answer key
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells make proteins. Proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells, and they are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes.
Protein synthesis occurs in two steps: transcription and translation. Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied into mRNA. Translation is the process by which mRNA is used to make a protein.
Transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and separates the two strands of the DNA molecule. RNA polymerase then uses the DNA as a template to synthesize a complementary mRNA molecule.
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. The mRNA molecule binds to a ribosome. The ribosome then reads the mRNA molecule and uses the information in the mRNA to synthesize a protein.
Mutations and Genetic Disorders
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to radiation, chemicals, and errors in DNA replication.
Mutations can have a variety of effects on the organism. Some mutations are harmless, while others can be harmful or even fatal. Harmful mutations can lead to genetic disorders, which are diseases that are caused by changes in the DNA.
There are many different types of genetic disorders. Some of the most common genetic disorders include sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Huntington’s disease.
- Sickle cell anemiais a genetic disorder that affects the hemoglobin in red blood cells. Hemoglobin is the protein that carries oxygen in the blood. In people with sickle cell anemia, the hemoglobin is defective, which causes the red blood cells to become sickle-shaped.
- Cystic fibrosisis a genetic disorder that affects the lungs, pancreas, and other organs. Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene, which codes for a protein that helps to regulate the flow of salt and water in the body.
- Huntington’s diseaseis a genetic disorder that affects the brain and nervous system. Huntington’s disease is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene, which codes for a protein that is involved in the development of the brain.
Quick FAQs
What is the primary function of DNA?
DNA serves as the genetic blueprint, carrying instructions for all cellular activities and traits.
How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA is single-stranded, contains uracil instead of thymine, and plays a crucial role in protein synthesis.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are cellular structures that facilitate the translation of mRNA into polypeptide chains, which eventually fold into functional proteins.