Delving into the realm of scientific communication, the language of science worksheet answers serves as a valuable guide, empowering individuals to navigate the complexities of scientific discourse. This comprehensive resource provides a solid foundation for understanding the precise and objective language that underpins scientific inquiry, enabling effective comprehension and dissemination of scientific knowledge.
Through a structured approach, the worksheet delves into the significance of using precise and unambiguous language in scientific communication, offering a comprehensive glossary of common scientific terms and their meanings. By providing strategies for interpreting complex scientific concepts and engaging with scientific literature, this resource equips learners with the tools necessary to confidently engage with the language of science.
1. Defining the Language of Science
The language of science is precise and objective, using specific terms and avoiding ambiguous or subjective language. This ensures that scientific communication is clear and unambiguous, allowing for accurate interpretation and replication of experiments.
Examples of Scientific Terms, The language of science worksheet answers
- Hypothesis:A proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on evidence and observation.
- Theory:A well-substantiated explanation of a natural phenomenon, supported by a body of evidence.
- Variable:A factor that can change in an experiment, either independently (independent variable) or dependently (dependent variable).
Importance of Avoiding Ambiguous or Subjective Language
Ambiguous or subjective language can lead to misinterpretation and confusion in scientific communication. For example, terms like “large” or “small” are relative and can vary depending on the context, making it difficult to compare results across studies.
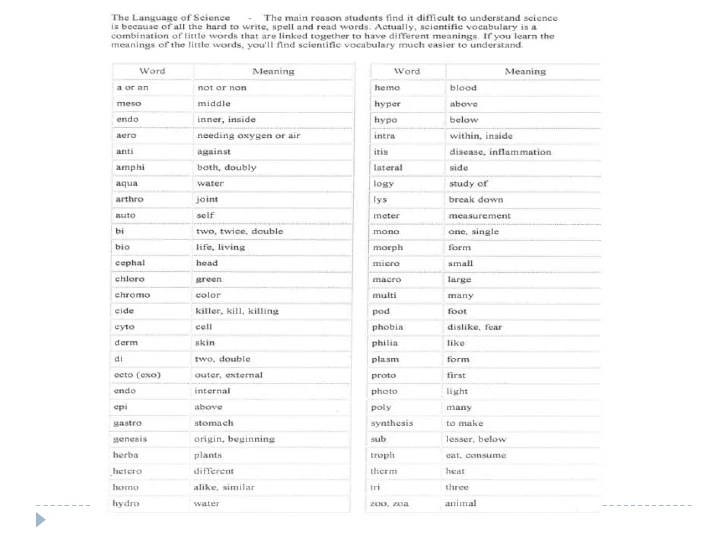
2. Understanding Scientific Vocabulary
Glossary of Common Scientific Terms
Here is a glossary of common scientific terms and their definitions, organized into categories:
| Category | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Biology | Cell | The basic unit of life, consisting of a membrane-bound nucleus and cytoplasm. |
| Chemistry | Atom | The smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties. |
| Physics | Energy | The ability to do work or produce change. |
Examples of Scientific Terms in Use
These terms are used in scientific texts to convey specific concepts and ideas:
“The cell is the fundamental unit of life, responsible for all biological functions.”
“Atoms are the building blocks of matter, consisting of a nucleus and electrons.”
“Energy is conserved in all physical processes, meaning it cannot be created or destroyed.”
3. Interpreting Scientific Texts
Strategies for Comprehending Complex Scientific Concepts
- Read actively:Engage with the text, highlighting key terms and concepts.
- Use context clues:Infer meaning from the surrounding text and diagrams.
- Relate to prior knowledge:Connect new information to existing knowledge.
Role of Context and Prior Knowledge
Context and prior knowledge play a crucial role in understanding scientific texts. The context provides clues about the meaning of unfamiliar terms, while prior knowledge helps connect new information to existing schemas.
Exercise: Interpreting Scientific Texts
Analyze the following scientific text and identify the main concepts and their relationships:
“Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. This process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, where chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and converts it into chemical energy.”
4. Communicating Scientific Findings
Formats for Scientific Communication
- Research papers:Formal reports of original research findings.
- Presentations:Oral or poster presentations at conferences or meetings.
- Scientific articles:Articles published in peer-reviewed journals.
Importance of Clarity, Conciseness, and Organization
Clarity, conciseness, and organization are essential for effective scientific writing. Clear language ensures that the message is easily understood, conciseness avoids unnecessary details, and organization helps readers follow the logical flow of the text.
Template for Structuring a Scientific Report
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Methods
- Results
- Discussion
- Conclusion
5. Engaging with Scientific Literature: The Language Of Science Worksheet Answers
Comparison of Scientific Journals
Different scientific journals target specific audiences and publish research in different fields. Here is a comparison of some major journals:
| Journal | Target Audience | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | General science community | Multidisciplinary research |
| Science | General science community | Multidisciplinary research |
| Cell | Biologists | Cell biology |
| Physical Review Letters | Physicists | Physics research |
Tips for Searching and Accessing Scientific Databases
- Use specific s:Search for relevant terms related to your topic.
- Explore different databases:Utilize multiple databases to increase your search results.
- Utilize university libraries:Access online databases and resources through university subscriptions.
Role of Peer Review
Peer review is a process where scientific research is evaluated by experts in the field. It ensures the accuracy, credibility, and validity of scientific information.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of using precise language in scientific communication?
Precise language ensures clarity and eliminates ambiguity, allowing for accurate interpretation and dissemination of scientific findings.
How can I improve my understanding of scientific vocabulary?
Utilize a scientific glossary, consult textbooks, and engage in discussions to expand your scientific vocabulary and enhance your comprehension.
What strategies can I employ to interpret complex scientific concepts?
Employ context clues, leverage prior knowledge, and seek clarification from experts to unravel the complexities of scientific concepts.